MODULE 5 - Women and the Energy Transition
The Indian Energy Transition Series
Women and Energy Transition | Module 5 | The Indian Energy Transition Series - Heinrich Böll Stiftung Delhi
 Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
MODULE 5 - Women and the Energy Transition
(Playtime - 5:20)
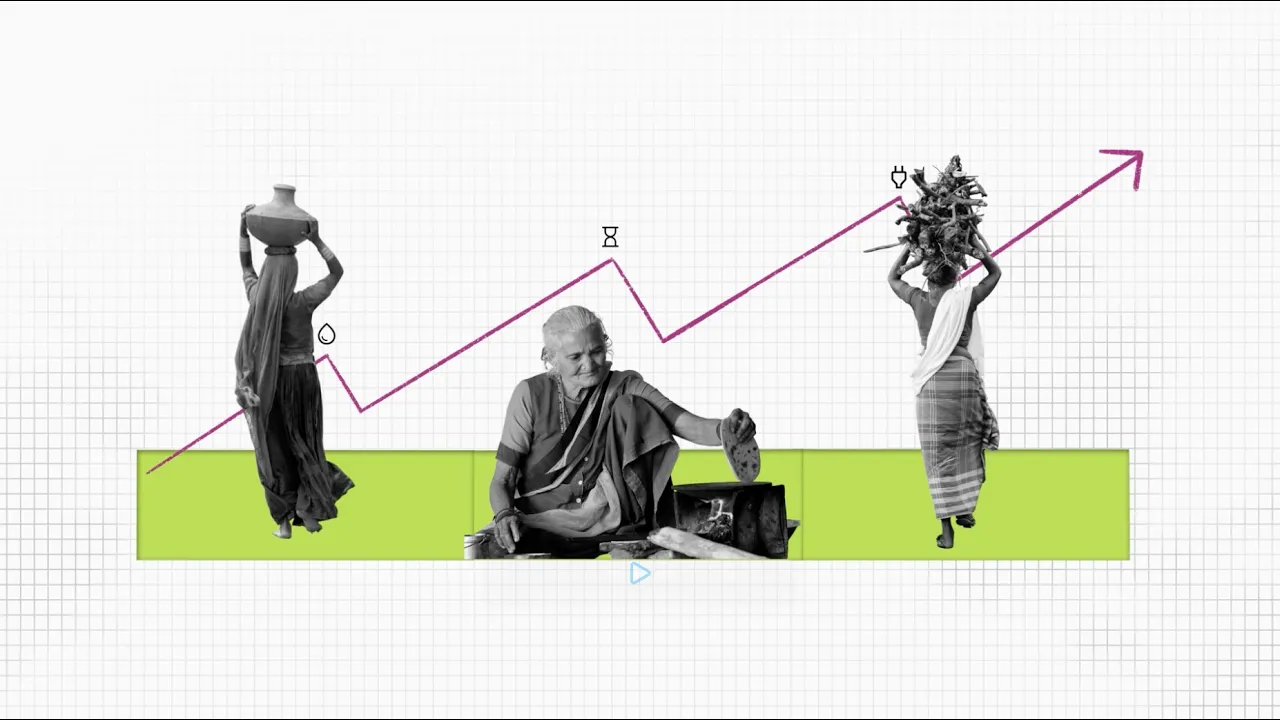
This video explores where the energy transition meets gender equality, highlighting the challenges women face in access, representation, and jobs, and how a gender-just transition can create new opportunities.
-
Energy transition can advance gender equality
-
Women face disproportionate energy poverty
-
Women are underrepresented in the energy workforce
-
Clean energy access improves health & economic mobility
-
Decentralized renewables can transform women’s livelihoods
Energy Poverty
Lack of reliable electricity access limits economic opportunities and education.

Health Risks
Indoor air pollution from biomass cooking affects millions of women globally.

Economic Disparity
Persistent wage gaps and fewer leadership positions in energy sectors.

Limited Voice
Minimal representation in policy-making and community energy decisions.

The ability of women and girls to take action and build resilient futures depends on removing structural and systemic barriers and closing gender gaps.
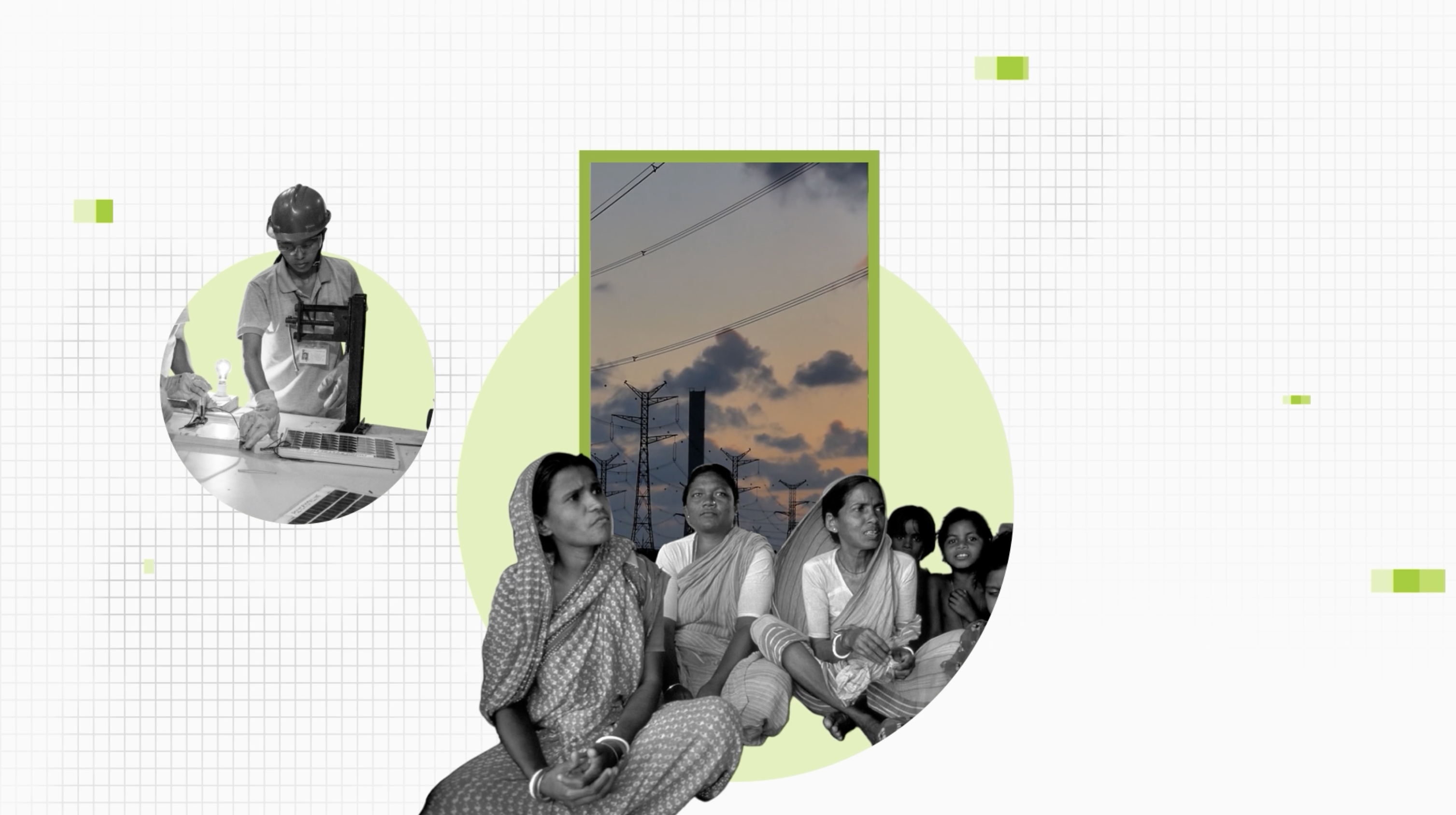
Electrified, Gaps Persist
More than 900 million people have gained electricity access, but energy poverty and reliability gaps persist.
Women in Renewable Energy
Women make up only 11% of India’s renewable energy workforce, far below the global average of 32%.
Gender Pay Gap
Women in the energy workforce earn on average 15% less than men.
Policy Spaces
Create inclusive forums for women's voices. Ensure representation in decision-making bodies. Design participatory planning processes.
Financial Resources
Guarantee adequate funding for gender initiatives. Direct resources to women-led enterprises. Remove economic barriers to participation.
Skills Training
Provide technical education and capacity building. Develop gender-responsive training programs. Bridge the knowledge gap.
Enabling Environment
Foster secure workplaces and supportive policies. Address systemic discrimination. Build institutional support structures.
Further Readings