MODULE 3 - Sectoral Actions for Energy Transition
The Indian Energy Transition Series
Sectoral Actions for Energy Transition | Module 3 | The Indian Energy Transition Series - Heinrich Böll Stiftung Delhi
 Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
Module 3 -Sectoral Actions for Energy Transition
(Playtime - 5:51)
This video breaks down how India’s major sectors — industry, transport, buildings, MSMEs, and agriculture can shift to cleaner energy, and why some sectors are easier to decarbonize than others.
-
India’s major sectors—industry, transport, buildings, MSMEs, and agriculture—must transition differently for the country to meet its clean energy goals
-
Electrification can cut emissions in many areas, but heavy industries need additional solutions like green hydrogen
-
MSMEs represent one of India’s biggest opportunities for fast, cost-effective clean energy adoption
-
Growing cities and rising cooling demand require efficient, renewable-powered buildings and urban systems
-
Rural India can significantly reduce fossil fuel dependence through solar irrigation, micro-grids, and decentralized renewables
-
Smart planning, supportive policies and the right technologies are key to driving a balanced, affordable, sector-wise transition
Why Sectoral Action Matters
India’s energy transition has three major goals:
-
Achieve net zero
-
Increase renewable energy generation
-
Shift citizens and industries to cleaner energy
But as the economy grows, energy demand is rising — making it essential to reshape how individual sectors use energy.
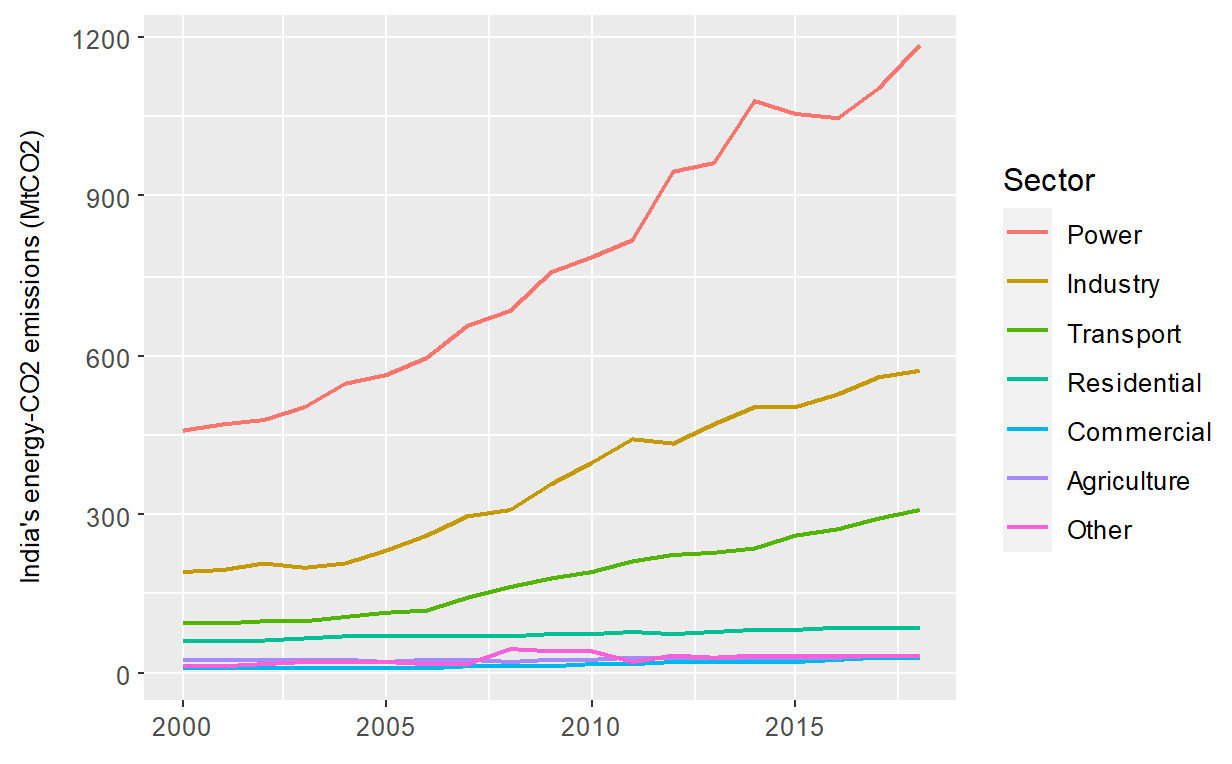
Heavy industries require very high temperatures and currently depend on fossil fuels, often with facilities located close to coal resources. This makes reducing emissions in these sectors particularly challenging. Decarbonising them is costly, and today’s low-carbon solutions are still limited in scale and maturity. Even so, green hydrogen is emerging as a promising option for the future.
63.3 M
MSMEs in India
Micro, small, and medium enterprises across the nation.
Manufacturing Sector
MSMEs in India operating in the manufacturing sector (e.g. pharmaceuticals, steel forging, and textiles sectors).
Share of Industrial Energy Use
MSMEs account for roughly one-quarter of India’s industrial energy consumption, a major lever for decarbonisation.
India's 63.3 million MSMEs represent a transformative opportunity. Many operate in industrial clusters with shared infrastructure.
These enterprises don't require high-temperature fossil fuels. They can adopt clean energy solutions quickly and cost-effectively.
Rooftop Solar
On-site renewable generation reducing grid dependency.
Efficient Machinery
Energy-smart equipment lowering operational costs.
Green Logistics
Electric transport for supply chains and distribution.

Smart Buildings
Energy-efficient design and climate control systems.
EV adoption is accelerating steadily. Multiple vehicle segments are transitioning simultaneously.
Global EV penetration was 16.48% in 2024, whereas India’s rate was 7.66%, underscoring the gap India must bridge to meet its 30% target by 2030.
India’s Future Infrastructure Yet to Be Built
Most of India’s 2047 urban infrastructure is still ahead — shaping long-term energy demand.
Megacities
Urban expansion will sharply increase energy use in homes, offices, and public buildings.
Buildings Consume a Third of India’s Electricity
Homes and commercial buildings together account for nearly one-third of India's total electricity use.
Energy-Efficient Design
Buildings incorporating passive cooling, natural ventilation, and thermal insulation.
Renewable-Powered Spaces
Commercial buildings generating their own clean electricity on-site.
Climate-Resilient Planning
Smart, integrated urban systems designed for extreme weather events.
Decentralised renewable solutions can transform rural energy use. These technologies offer independence from unreliable grids.
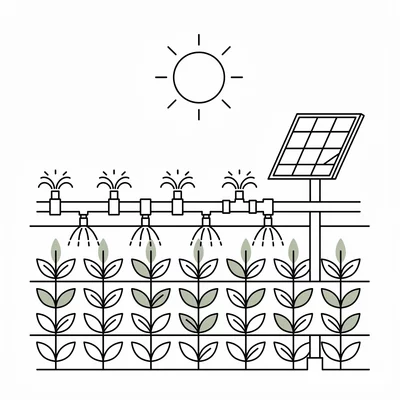
Solar-Powered Irrigation
Reliable, cost-effective water pumping for farms.
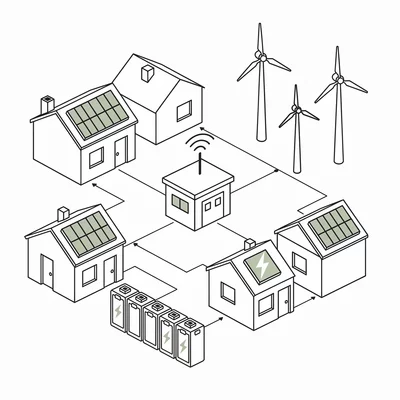
Micro-Grids
Community-level renewable electricity distribution systems.
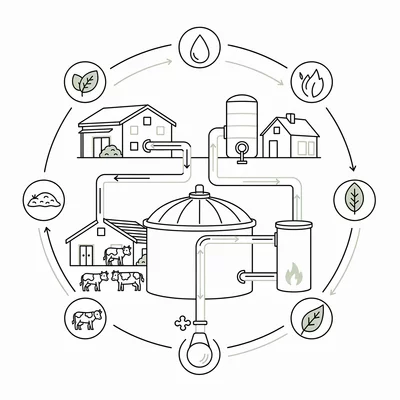
Biogas Plants
Converting agricultural waste into cooking fuel.
Solar Powered Dryers & Cold Storage
Preserving crops using renewable-powered systems.
Further Readings